Question
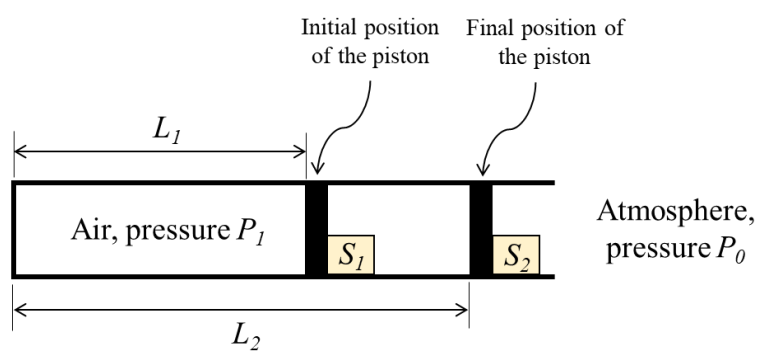
Consider a fully adiabatic piston-cylinder arrangement as shown in the figure. The piston is massless and cross-sectional area of the cylinder is 𝐴. The fluid inside the cylinder is air (considered as a perfect gas), with γ being the ratio of the specific heat at constant pressure to the specific heat at constant volume for air. The piston is initially located at a position 𝐿1. The initial pressure of the air inside the cylinder is 𝑃1 ≫ 𝑃0, where 𝑃0 is the atmospheric pressure. The stop S1 is instantaneously removed and the piston moves to the position 𝐿2, where the equilibrium pressure of air inside the cylinder is 𝑃2 ≫ 𝑃0.
What is the work done by the piston on the atmosphere during this process?
Options :
0
𝑃0𝐴(𝐿2 − 𝐿1 )
𝑃1𝐴𝐿1 ln( 𝐿1/ 𝐿2)
(𝑃2𝐿2 − 𝑃1𝐿1)𝐴 /(1 − γ)
Answer :
𝑃0𝐴(𝐿2 − 𝐿1 )
Solution :
From the given data, V1= L1 x A
V2=L2x A
Watm = Po(V2 - V1)
= Po(L2A — L1A)
= PoA(L2 - L1)