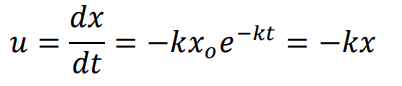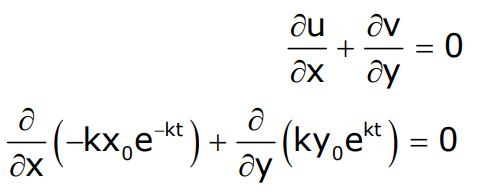Question
In a Lagrangian system, the position of a fluid particle in a flow is described as 𝑥 = 𝑥𝑜𝑒 −𝑘𝑡 and 𝑦 = 𝑦𝑜𝑒𝑘𝑡 where t is the time while 𝑥𝑜, 𝑦𝑜, and k are constants. The flow is
Options :
unsteady and one-dimensional
steady and two-dimensional
steady and one-dimensional
unsteady and two-dimensional
Report
More Similar Tests